If the Revit plugin is not installed on your computer, you can first go to the article “ Autodesk REVIT Plug-in - Installation ” and then come back here after this operation.
Tip: To fully follow the instructions in this article, we recommend adding a scatterplot first. If this is not done, go to the article “ Autodesk REVIT Plug-in – Insert a point cloud ”
The “Point Cloud Manager” is a graphical interface allowing to modify the parameters of each point cloud of the Revit project from the website. This window allows to move, to resize the interface as well as to anchor it to one side of the Revit screen.
To begin, click on a point cloud located in the “Point Cloud Manager” window. If the interface is not displayed, click on the “Point Cloud Manager” button located in the “Cloud” toolbar in the “Add Point Cloud” category.
Part of the “Point Cloud Manager” interface appeared. The interface is split like this:
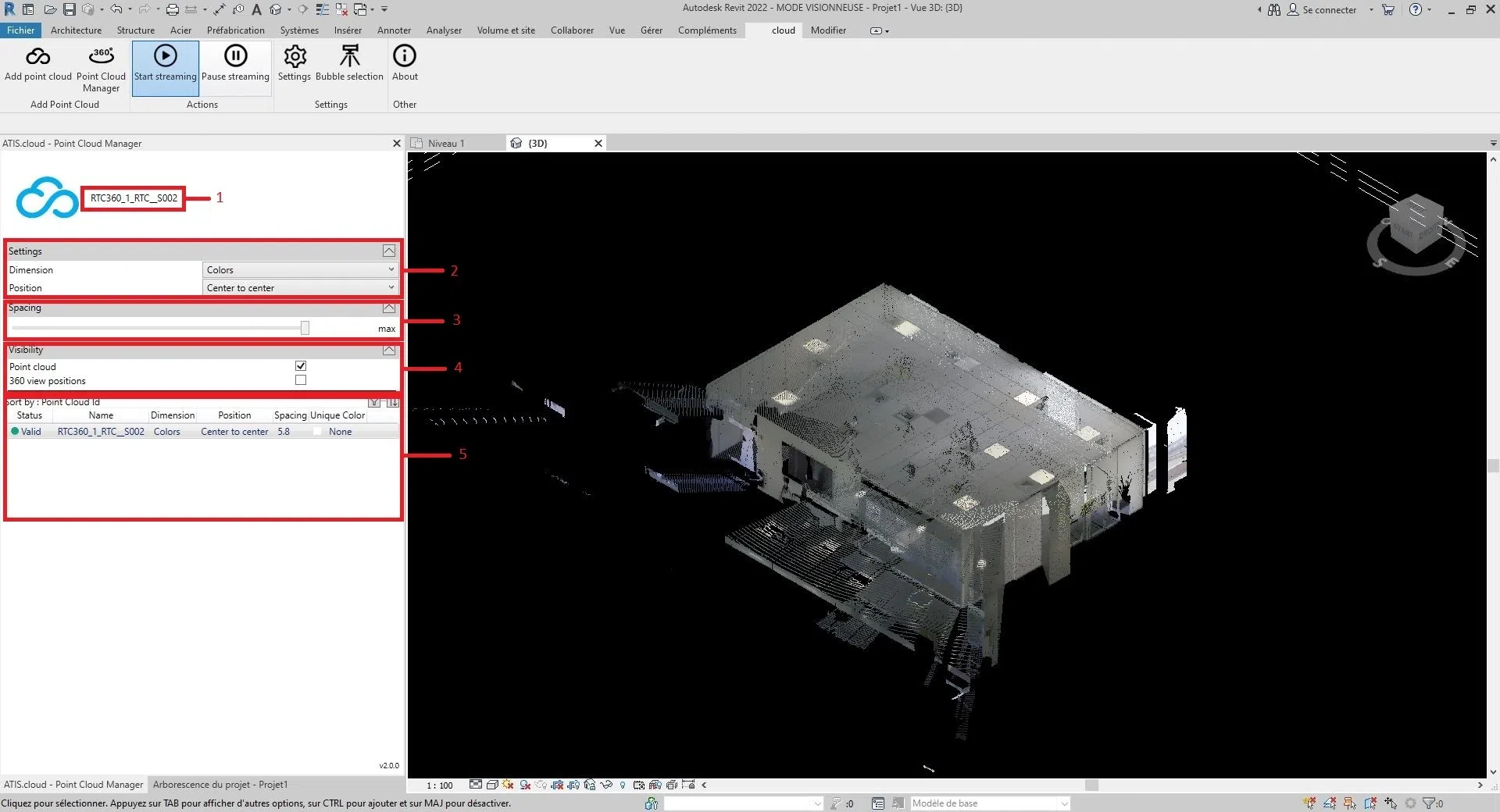
1: Name of the cloud selected, the name displayed is the same as that of the web project
2: Characteristics of the cloud such as the dimension and the position of the cloud
3: Spacing of each point of the cloud
4: Point cloud and scanners visibility parameter (for more information on scanners, go to the article “Scanner Revit”)
5: All the clouds inserted through the Revit plugin, it allows to see at a glance the main parameters of each cloud as well as to sort them.
- Trick :
- You can fold and unfold sections using the arrow button to the right of each section;
- You can resize the size between part 6 and the rest by holding down and then moving the mouse over the black bar located between the “Visibility” section and part 6.
You can now modify each parameter of each point cloud.
- The dimension of the cloud, go to the section “Change the dimension”;
- The position of the cloud, go to the section “Edit position”;
- The distance between the points of the cloud, go to the section “Modify the spacing”;
- The visibility of the cloud or scanners, go to the “Change visibility” section.
Change dimension:
To modify the selected dimension, click on the selection box to the right of “Dimension”.
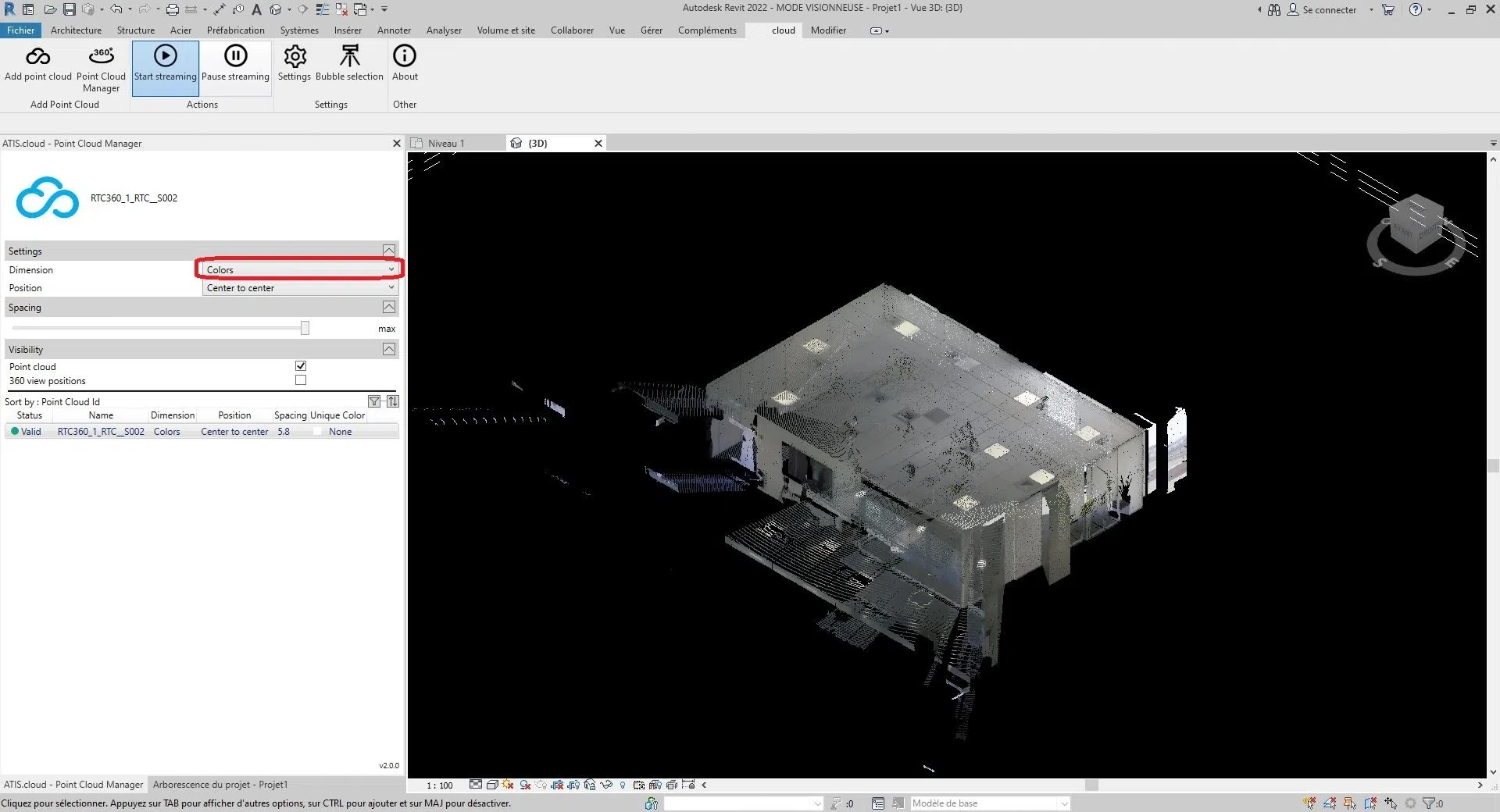
There are six sizes to choose from:
Colors, Intensity, Classification, Height, Point Source ID and Unique Color.
- Colors : It is used to represent the color of each point in the point cloud. The red, green, and blue channels are used to represent the color of the dot, while the alpha channel is used to represent the transparency or opacity of the dot. The use of color in LiDAR point clouds can be useful for visualization and interpretation purposes, as it can provide additional information about the properties of the objects and surfaces represented by the points. For example, in vegetation mapping, the color of the points can be used to distinguish between different types of vegetation or to identify areas with high or low vegetation density.
- Intensity : It represents the strength or amplitude of the signal that was received by a sensor or device when the point was captured. In some cases, the intensity is related to the reflectance of the object at that point. For example, in a LiDAR point cloud, the intensity value represents the amount of laser light that has been reflected back to the sensor by the object. In this case, a higher Intensity value would indicate a surface that reflects more light, such as a white wall, while a lower Intensity value would indicate a surface that reflects less light, such as a black car. In other cases, the intensity may represent a different physical quantity. For example, in a photographic point cloud, intensity can represent the brightness of a pixel in the original image that was used to generate the point cloud.
- Classification : Will only work with compatible point clouds . The purpose of classification is to group similar points into meaningful categories, such as soil, vegetation, buildings, and other objects.
- Height : It represents the height or vertical position of each point. Elevation data is important in many point cloud applications, such as topographic mapping, flood modeling, urban planning, and infrastructure design. By analyzing elevation data, it is possible to create accurate and detailed digital elevation models (DEMs) that can be used for a wide range of geospatial analysis and visualization purposes.
- Point Source ID : This identifies the specific laser sensor that generated the point. Each laser sensor in a LiDAR system has a unique identifier or number, and this information is recorded in the point cloud data to enable analysis and quality control. Point source identification is especially useful in situations where multiple LiDAR sensors are used to capture a single scene or area. By identifying which sensor generated each point, it is possible to perform quality checks on the data and ensure that the data is correctly aligned and registered between the different sensors. This is especially important in applications such as forestry, where multiple LiDAR sensors can be used to capture data from different angles and perspectives. On our platform, the point source id is used to store the source analysis id, allowing users to easily track which analysis each point in the point cloud originated from. For example, if multiple scans were performed on the same area using a 3D laser scanner, each scan could be assigned a unique scan ID and the point source ID attribute for each point in the cloud points could be set to the corresponding scan ID.
- Unique Color: The objective of the “Unique Color” dimension is to be able to color the point cloud with a unique color defined by the user.
Change position:
To modify the selected position, click on the selection box to the right of “Position”.
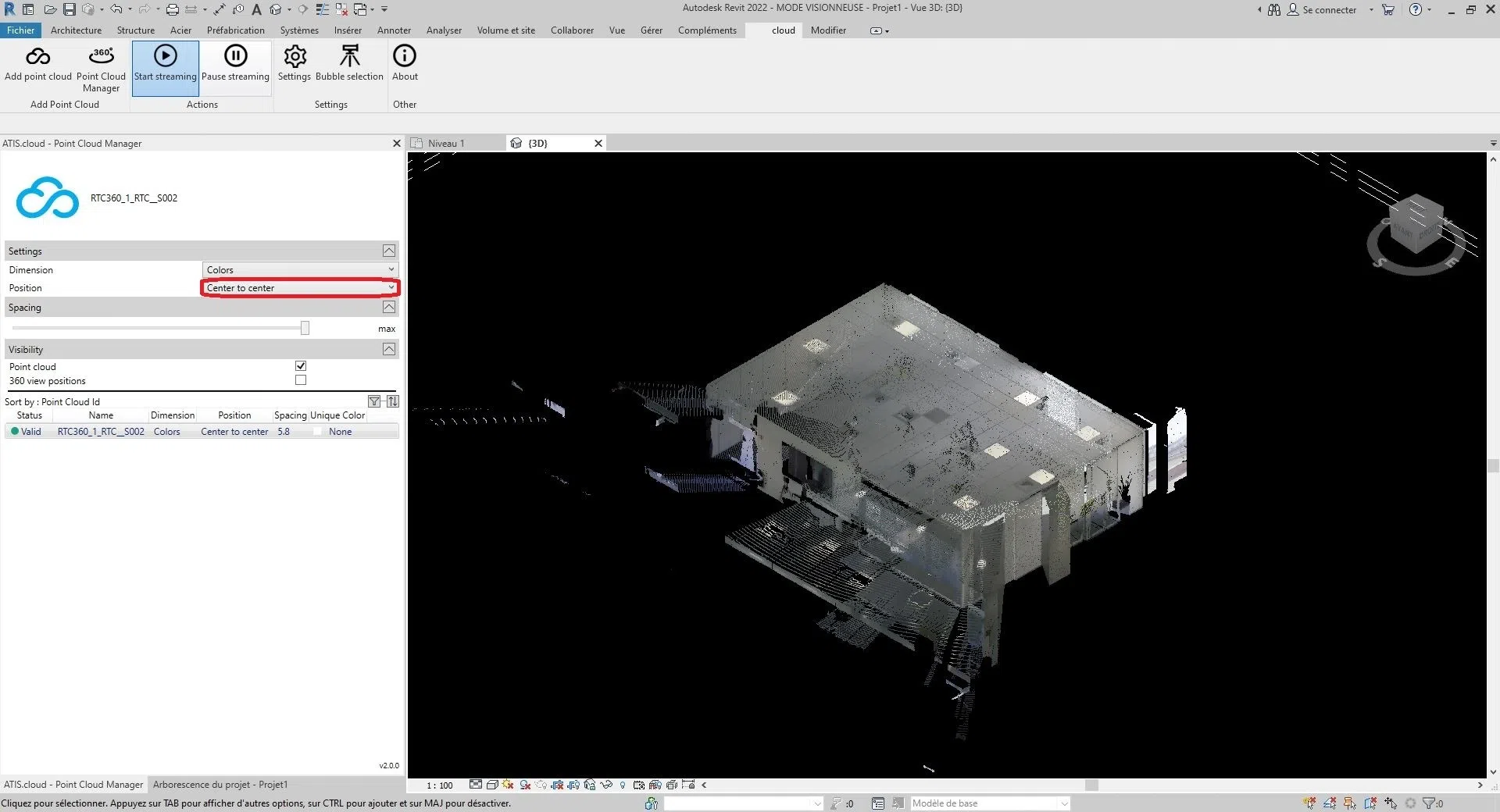
You will have the choice between these three options:
"Center to Center", "Internal Origin", or "At the Shared Site".
- Center to Center : This option places the point cloud using the center of the viewport as a reference point.
- Internal origin : This option positions the point cloud using the internal origin of the cloud as a reference point. The internal origin is usually defined by the coordinate system of the point cloud itself. Using this option, the point cloud will be positioned according to its internal origin rather than the origin of the Revit project. This can be useful when you need to align the point cloud to its own internal coordinate system.
- At the shared site : This option places the point cloud at the location of the shared site. Shared site refers to a common geographic location on which multiple projects can be based. Using this option, the point cloud will be positioned according to the coordinates of the shared site. This can be useful when working on projects based on a common site and want to align the point cloud to that shared location.
- Auto – Origin to Last Placed : Revit places the next imported point cloud consistently with the previously imported point cloud. This option becomes activated after inserting a first point cloud. You can move this first cloud, for example, in order to align it correctly with the elements of the model. If you have additional point clouds created on the same site and in the same coordinate system as the first one, it is recommended to use this option to insert the additional point clouds. The new point clouds will then be correctly positioned relative to the first.
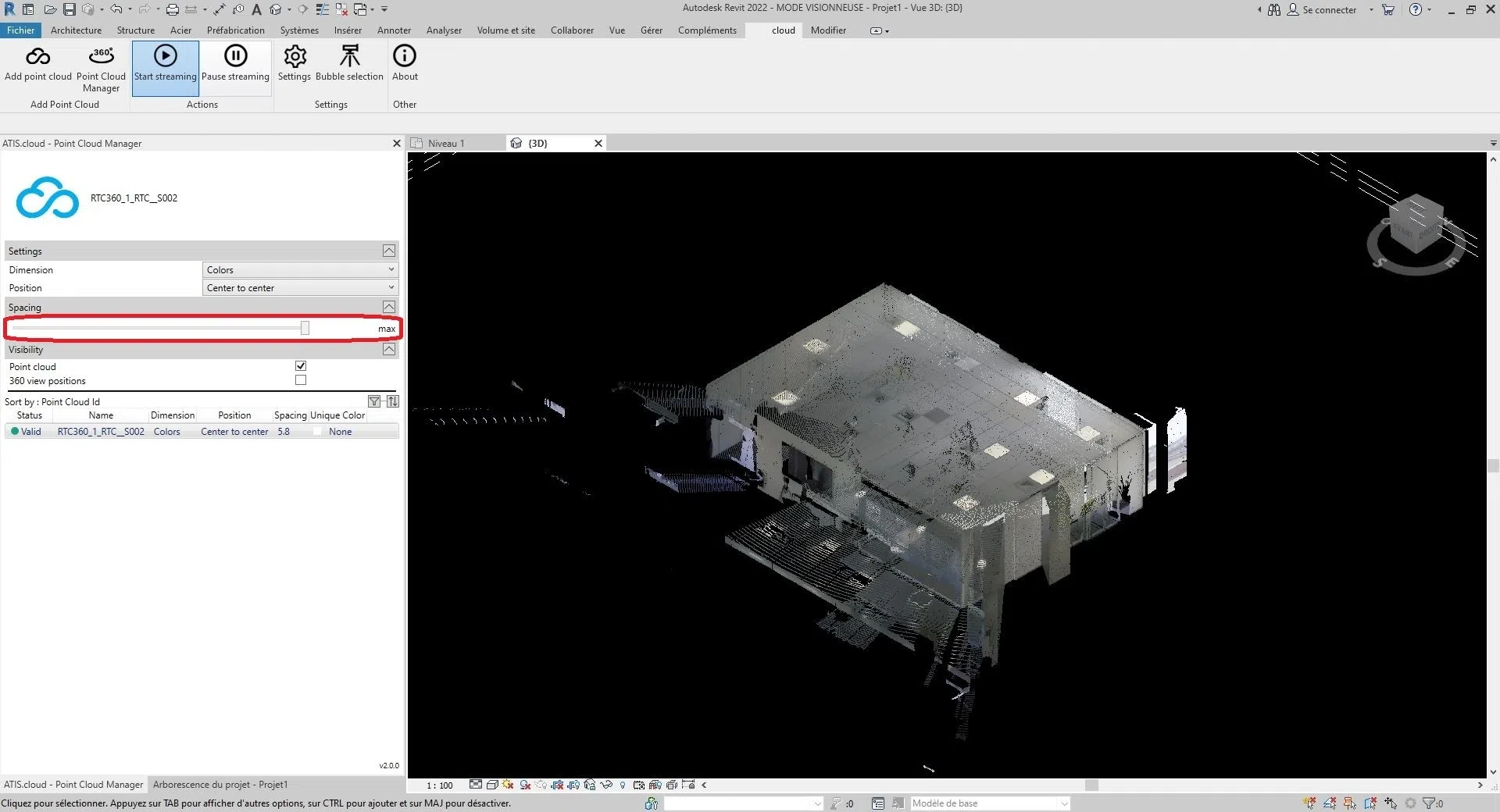
Change spacing:
To modify the spacing between the points of the cloud, move the bar of the “Spacing” section.
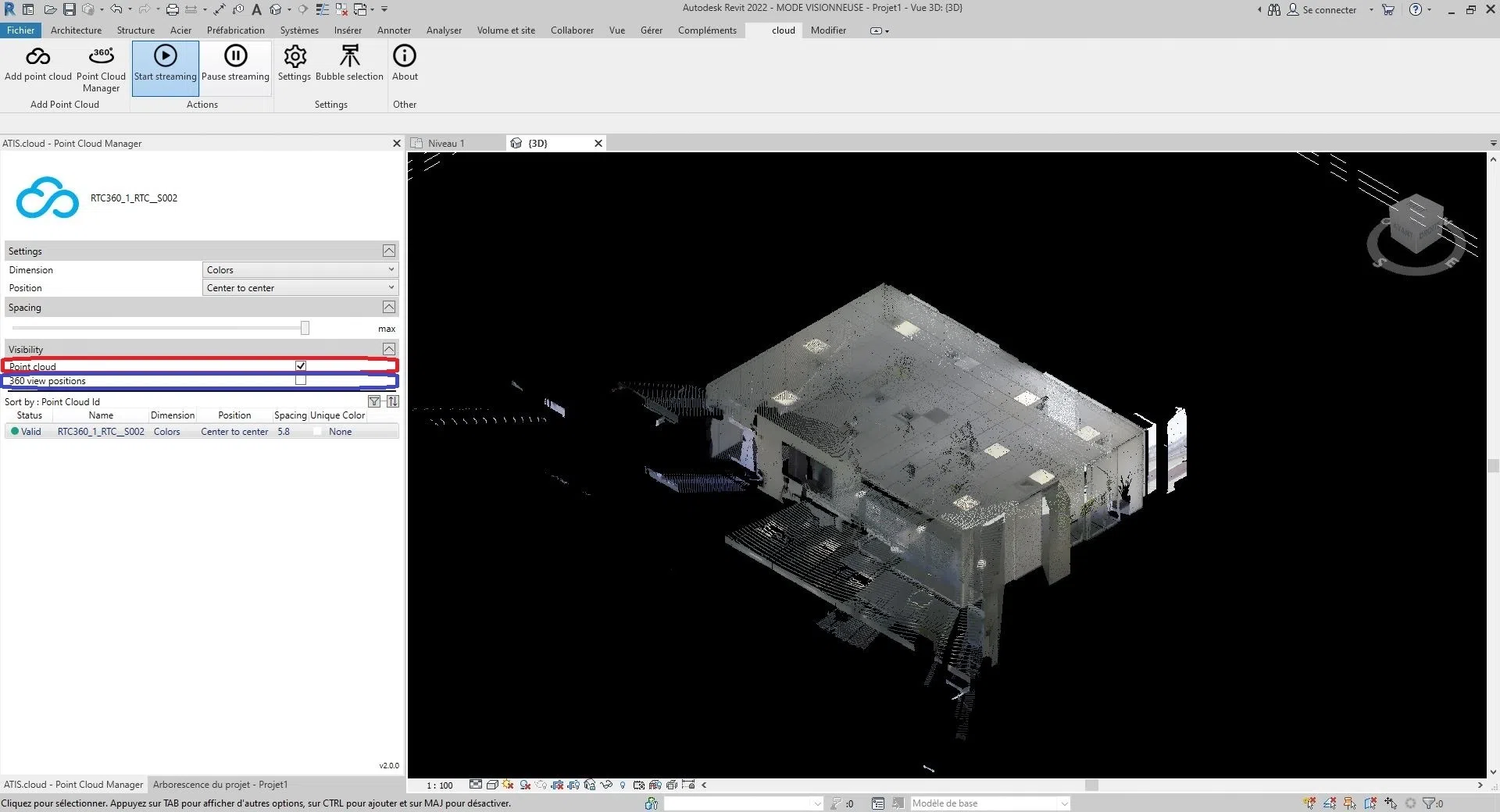
Change visibility:
To change the visibility, you have two options. Or, you can show/hide the point cloud by checking/unchecking the box to the right of “Point Cloud” in the “Visibility” section. Or, you can show/hide the point cloud scanners by checking/unchecking the box to the right of “360 View” in the “Visibility” section. (The visibility is the same between the different views of the project)
- Tips:
- Scanner information is in the “ Bubble management ” category.
- To zoom on a point cloud in the viewer, simply double-click on the corresponding cloud.
Congratulation ! You know everything about the “Point Cloud Manager” interface.
If you run into any issues, our support team is here to help. Happy exploring!